The Ultimate Guide to Business Cyber Insurance in Canada
By Arthur Dubois | Published on 02 May 2023

If your business needs internet, you need cyber insurance. Why? Cyber attacks and threats are on the rise. According to the Allianz Risk Barometer, cyber security is the biggest concern for global companies in 2022. This is striking, given the continued supply chain, inflation, and post-pandemic issues plaguing the Canadian and international economies. This concern is largely due to the fact cyber attacks have become existential business risks that can cause companies large and small to fail.
Without cyber insurance, you could lose everything you’ve worked so hard to build. This ultimate guide cuts through the noise to give business owners the information they need to understand cyber security risks and how they can protect their businesses with cyber insurance.
A scary statistic
Did you know that 60% of small businesses fold within six months after being the victim of a cyber attack? Cyber attacks can cause enough financial and reputational damage that a once successful business can no longer operate. Given this, it’s no surprise that Canadian businesses spent over 10 billion dollars on cyber security in 2021.
What is Business Cyber Insurance
It is important to cover some basic business cyber insurance information before getting into the details. To begin with, cyber insurance, also known as cyber liability insurance or cybersecurity insurance, protects businesses with both first-party and third-party liability coverage due to cyber attacks and data breaches.
Cyber attacks and data breaches are often used synonymously; however, it’s important to clarify that a data breach is any unauthorized disclosure of sensitive data, whether intentional or not, and can occur without a cyber attack.
First Party Coverage
A business, aka the insurance policyholder, is the first party in an insurance policy. The insurer, aka the company providing the insurance, is the second party. There are different types of cyber attacks and data breach events that a business cyber insurance policy provides coverage for, and may include financial losses and expenses incurred due to:
- Cyber extortion or ransom
- Business interruptions
- Identity theft
- Data loss
- Legal costs
- Reputation management
- Credit monitoring
- and more
Third Party Coverage
Third parties to a cyber business attack or data breach are generally the customers or clients of the business that are either financially impacted or financially exposed by a cyber attack or data breach.
Exposed means they are now open to potential financial loss or costs. The list of major and well-known corporations that inadvertently exposed sensitive client, customer, or employee information is eye-opening. The list includes businesses such as Facebook, Toyota, Equifax, Ikea, the list goes on.
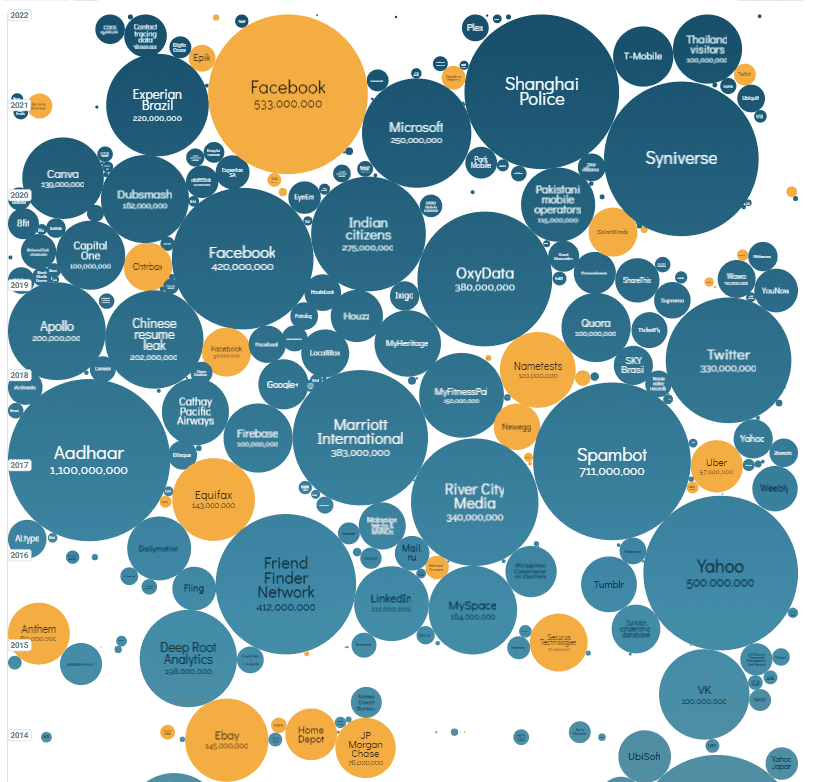
Photo credit: informationisbeautiful.net
Third party coverage can protect businesses from direct costs due to third party lawsuits and settlements, damages determined by the courts, government and regulatory fines and penalties, credit monitoring for individuals with breached information, public relations costs, etc.
Do small and medium-sized businesses need cyber liability insurance?
The short answer is yes because nearly all businesses, including small and medium-sized businesses, have exposure to cyber attacks and data breaches. Specifically, this exposure is created when a business has one of the following:
- They store on a computer or the cloud sensitive data such as customer credit cards and banking information
- They use an electronic point-of-sale system
- They have access to their client’s computers and internal systems such as an intranet
In today’s business environment, it would be difficult to find a business that wouldn’t have a degree of exposure due to cyber threats or data breaches.
How much does cyber liability insurance cost in Canada?
The cost of cyber insurance in Canada will vary depending on the size of the business and the industry they belong to. Cyber liability insurance will start at approximately $500 to $1,000 per year or more, depending on the assessed risk level.
How to save money on cyber liability insurance premiums
To save money on cyber liability insurance premiums you need to shop around and compare quotes from multiple providers. That can seem like a daunting task for a busy business owner, but you don’t necessarily have to do it all yourself.
An online insurance broker like Zensurance can save you a ton of time and money by doing the hard work for you. They have over 50 different insurance providers in their network and will compare quotes to find you the best possible price on cyber liability insurance premiums based on your needs.
Their online quoting tool is available to you 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. That means you can find the right cyber liability insurance policy for your business at the tap of a button. It only takes a few minutes and you don’t even need to make an appointment or talk to anyone. Zensurance will compare quotes for you so you can get back to business.
Is your business already covered for cyber liability?
Businesses may incorrectly think they are covered for cyber liabilities due to cyber attacks or data breaches with their existing commercial liability insurance. Considering the average cost of a cyber liability claim in Canada is $295,000, it is critically important for businesses to contact their insurance agent and inquire if they are currently protected from cyber liability, and to what extent.
How to add cyber liability insurance
Cyber liability insurance coverage can be purchased as a stand-alone cyber insurance policy in addition to an existing business insurance policy. However, cyber liability insurance can also be added to an existing business insurance policy through an endorsement also known as a rider. It is important to discuss what option makes sense for your business by consulting your insurance agent.
Three common cyber attacks
There is a long list of cyber attacks businesses can face, and it seems to be getting longer each year. Below are three common cyber attacks businesses face and must protect themselves from.
Phishing Attacks
Phishing attacks are a widespread form of cyber attack. The attacker pretends to be a trusted person or a representative from a trusted company and sends fake emails to a business. Once a link is clicked or an attachment is opened, the attacker can get access to confidential information and use it for a variety of damaging purposes.
To safeguard yourself and your business from phishing attacks, don’t open emails from people you don’t know, and update your passwords regularly.
Malware Attacks
Malware is short for malicious software viruses and includes ransomware, adware, spyware, and trojans. Ransomware, in particular, has become a significant cyber security threat for companies, and many companies have had to pay ransom to cyber attackers to regain access to their computer networks.
Protect yourself and your business from malware attacks by not clicking on suspicious links and downloads, and be cautious when using and sharing USB drives.
Password Attacks
Password attacks are when a hacker uses various tools and means to obtain business passwords. It’s not difficult to imagine the damage a hacker can cause with access to sensitive business accounts.
To safeguard yourself and your business from password attacks, create strong alphanumeric passwords, don’t share passwords, and update passwords frequently.
How Can Businesses Prevent Cyber Attacks?
The number of cyber attacks businesses have and will face continues to grow. However, businesses can reduce the likelihood that a cyber attack will be successful.
First, it’s recommended to frequently back up your business data and change your business passwords every couple of months. You should also ensure you use a password with a combination of at least ten characters, numbers, letters, and symbols.
Second, encrypt sensitive data and purchase a VPN for employees working from home or travelling often. Avoid saving credit card information online, and ensure all digital devices are updated to the latest operating system.
Finally, ensure everyone in your company is aware of cyber attack risks and what they should do and not do to prevent cyber attacks and data breaches. This is a critical step to prevent cyber attacks, but only 34% of employees at small to medium-sized businesses report receiving mandatory cyber security awareness training.
FAQs About Cyber Insurance in Canada
Unless a person has direct experience with cyber business insurance, they will likely find the available information on the internet to be confusing. Cyber insurance, also known as cyber liability insurance or cybersecurity insurance, protects businesses with both first-party and third-party liability coverage due to cyber attacks and data breaches. A business, the insurance policyholder, is the first party in an insurance policy, the insurer is the second party, and the third party is generally those customers or clients of the business that are either financially impacted or financially exposed by a cyber attack or data breach.
First Party Coverage
Businesses are the first party in a cyber liability insurance policy which provides coverage that may include financial losses and expenses incurred due to: cyber extortion or ransom, business interruptions, identity theft, data loss, legal fees, reputation management, credit monitoring, and more.
Third party Coverage
Third parties to a cyber business attack or data breach are generally the customers or clients of the business that are either financially impacted or financially exposed by a cyber attack or data breach. Third-party coverage can protect businesses from direct costs due to third party lawsuits and settlements, damages determined by the courts, government and regulatory fines and penalties, credit monitoring for individuals with breached information, and public relations costs.
Cyber insurance in Canada doesn’t typically cover costs to improve internal electronic systems after a cyber attack, the value associated with intellectual property theft, and the revenue or profits the business may not earn.
When a person or a business purchases a cyber insurance policy, they typically pay the policy premium 12 months in advance or will pay monthly. Cyber insurance protects the policyholder from losses due to cyber attacks that may include data branches, financial fraud, fraudulent transactions, identity theft, cyberbullying, etc. When a cyber attack is experienced and reported, the cyber insurance company will launch an investigation and will cover the costs associated with the damages incurred due to the attack.
Cyber liability insurance coverage can be purchased as a stand-alone cyber insurance policy in addition to your existing business insurance. However, it can also be added to your existing business insurance policy through an endorsement, also known as a rider. It is essential to discuss what option makes sense for your business by consulting your insurance agent.
Cyber insurance can be inexpensive, especially if bundled with other insurance coverage. The more coverage required by a business, the greater the cyber insurance cost. The average cyber insurance policy starts at approximately $500 per year, and businesses in specific industries, such as healthcare or finance, will start at approximately $1,000 or more.
The average cyber liability claim in Canada is $295,000.
Ransomware is when a cyber attacker demands a business pay a ransom to regain access to their computer systems. Ransomware payments are often included in cyber liability insurance; however, businesses should inquire with their cyber insurance provider to determine if their existing cyber insurance provides ransomware payment coverage.
Nearly all businesses have exposure to cyber attacks and data breaches and should have cyber insurance. Specifically, this exposure is created when a business has one or more of the following: they store sensitive data on a computer or the cloud, such as their customer’s credit card and banking information; they use an electronic point of sale system, or they have access to their client’s computers and internal systems such as an intranet. In today’s business environment, it would be difficult to find a business that wouldn’t have any exposure to cyber threats or data breaches.
