The Ultimate Guide to Car Insurance in Ontario
By Daniel Schoester | Published on 17 Jul 2023

Ontario residents pay an average of $1,655 per year on Car insurance, which is about $138 monthly. The most expensive city is Vaughn, with an average cost of $2,179. Smaller towns generally are the least costly, with Kendal costing $1,271 on average.
However, many more factors than your location determine the cost of insuring your car. In reality, insurance companies review your type of car, driving record, and personal information. They use this data to determine the probability you’ll need to make a claim. This calculates your monthly payment, otherwise known as a premium.
Since car insurance is mandatory in Ontario, understanding how it works is a massive benefit. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know to compare car insurance in Ontario, including the different types of coverage, where to get quotes, and the factors that influence your monthly payment.
Car Insurance In Ontario Explained
Auto insurance is required in Ontario because it provides financial protection when it isn’t your fault. If an accident injures you, you will receive compensation through a simplified process. This prevents the need to hunt down the person at fault, who may not pay you.
Claims & Deductibles
Your insurance company pools your monthly payment with other customers to form a fund. The insurance company will withdraw from the fund to cover your damages when necessary. However, they will only cover up to your policy amount, and you’ll have to pay the deductible. Your deductible is a pre-determined amount you’ll need to pay out of pocket when an accident happens.
Insurance Premiums
Your monthly payment is also known as your premium. Your premiums will increase if there’s a greater chance of making a claim. Additionally, your premiums will increase with more coverage. Not all coverages are mandatory in Ontario. However, you also don’t want to be in an accident without adequate coverage. As such, it’s essential to educate yourself on the different types of policies to determine what you need. The following section will explain the different types of car insurance coverage.
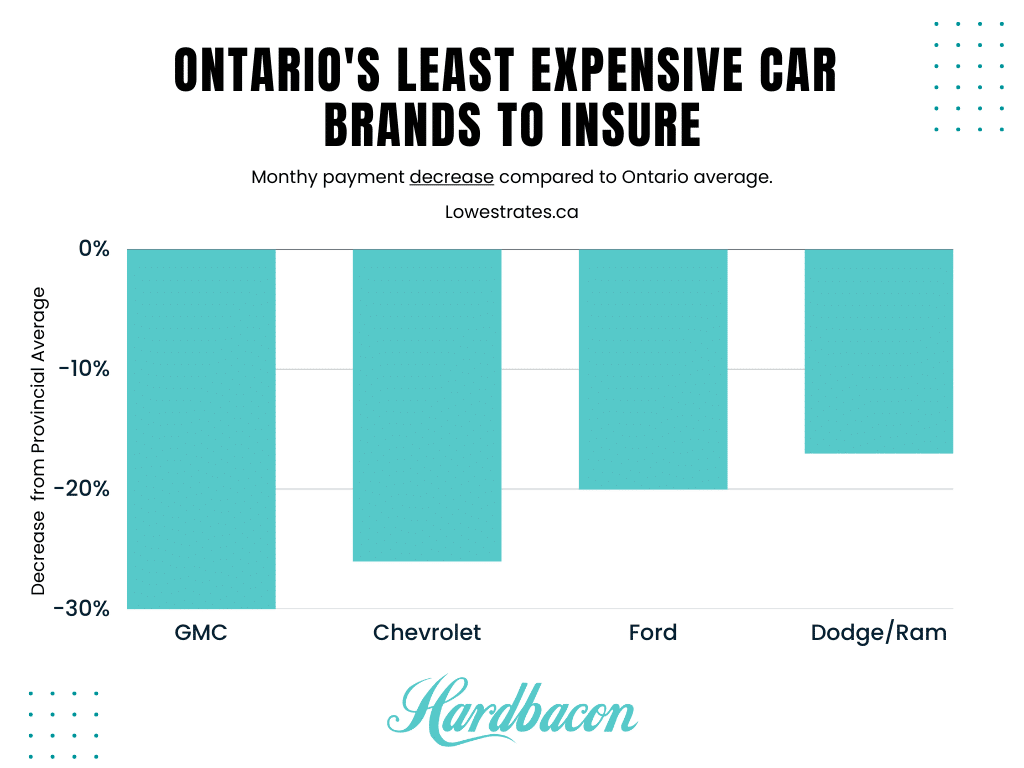
Source: Lowest Rates, 2022
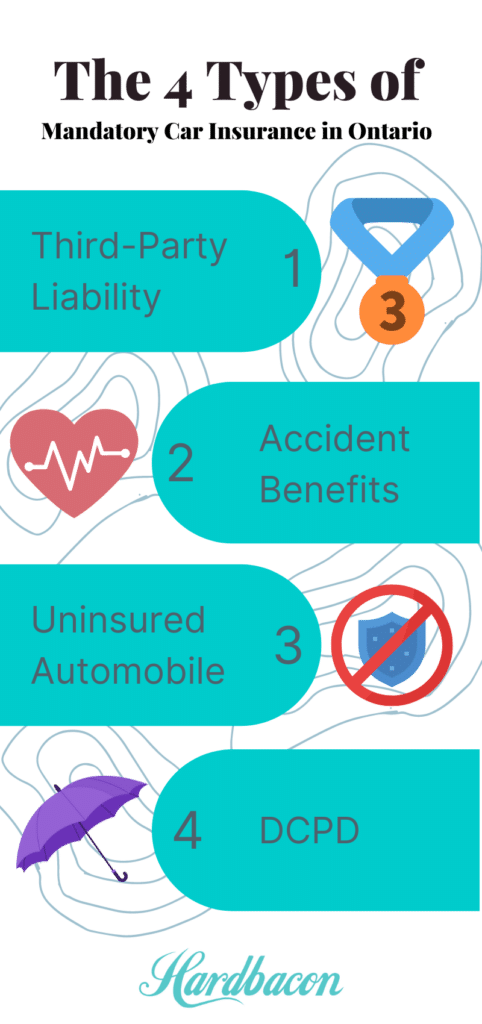
The Four Types Of Mandatory Car Insurance In Ontario
You’ll need four mandatory coverages to drive a car in Ontario. This includes third-party liability, accident benefits, uninsured automobiles, and direct compensation. While this section explains the mandatory coverages, the following discusses the optional coverages and add-ons. Canadians commonly use additional coverage, but you may not think they’re necessary.
1. Third-Party Liability Coverage
Third-party liability coverage pays for eligible damages and injuries to other people. This commonly includes medical bills, lost wages, and property damage. It will not cover your medical expenses or damage to your vehicle. To protect yourself in those cases, you would need additional coverage, such as collision or comprehensive coverage.
In Ontario, it is mandatory to have a minimum of $200,000 in third-party liability coverage. However, most people choose to have higher amounts for added protection. You could be personally responsible for the additional costs if the damages exceed your coverage limit.
2. Accident Benefits
Otherwise known as statutory accident benefits schedule (SABS), this coverage is to pay for your health treatment. This insurance commonly covers your medical expenses, rehabilitation costs, and lost wages if you or anyone in your vehicle is injured in an accident, regardless of who is at fault. However, you likely won’t receive compensation for injuries received while committing a crime or while driving under the influence of drugs or alcohol.
It’s different from the other mandatory policies because it only pays for the health treatment of yourself and your passengers. It’s different from third-party, which covers damages and injuries to the other person affected. It also shouldn’t be confused with collision coverage, which pays for damages to your vehicle.
In Ontario, it is mandatory to have a minimum of $65,000 in accident benefits coverage. It’s also worth noting that you may need more than the minimum coverage to fully protect yourself in a severe accident. If you need long-term medical care or rehabilitation, the costs can quickly increase and exceed your coverage limit.
3. Uninsured Automobile Coverage
Unfortunately, some people will drive vehicles without any insurance coverage. If they hit you and are at fault, they won’t have any insurance to pay for the damages. Sometimes, the other driver will leave the scene in a hit-and-run accident. In this scenario, their insurance won’t apply to you either.
As a result, uninsured automobile coverage will pay damages to you if the other person doesn’t have insurance. In Ontario, the minimum coverage is $200,000 for uninsured automobile coverage. However, you may choose to have higher coverage limits for added protection.
4. Direct Compensation Property Damage
Direct Compensation Property Damage (DCPD) covers repairs for your vehicle when you’re not at fault. It’s called direct compensation because you are paid directly by your insurance company. In other words, if you’re in an accident with someone else and their insurance company denies liability, DCPD can help you get the damages repaired or replaced.
In Ontario, it is mandatory to have a minimum of $200,000 in direct compensation property damage coverage. This coverage will not cover repair costs if you are at fault or the damages exceed your coverage limit. To protect yourself in those cases, you would need additional coverage, such as collision or comprehensive insurance.
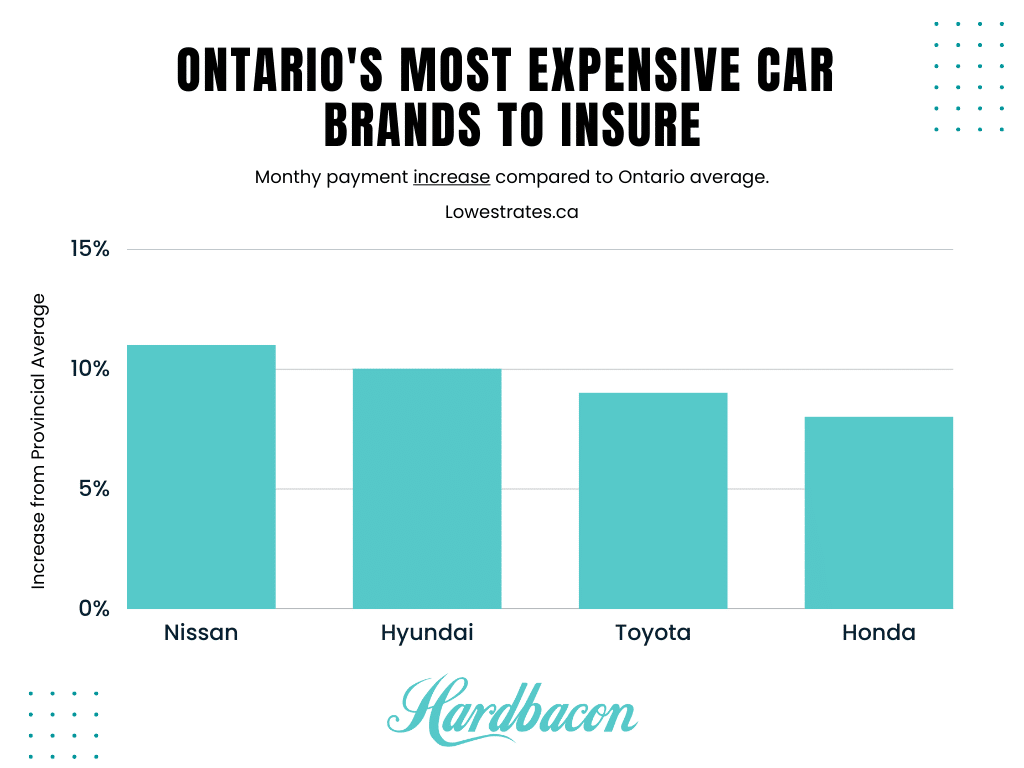
Source: Lowest Rates, 2022
Types Of Optional Car Insurance in Ontario
You can think of the mandatory options as the bare minimum protection in Ontario. They will only cover your health, along with the vehicle and health of the other party. If you’re at fault, your car will not be covered.
To fill the coverage gaps, there are additional types of insurance available. This section will explain the various types of automobile coverages and add-ons. However, enhancing your range will also increase your monthly payment.
Collision Coverage
Collision coverage pays for repairing or replacing your vehicle if it is damaged in a collision, regardless of who is at fault. This is different from third-party, which covers the other person’s property. In Ontario, collision coverage is optional and purchased in addition to the mandatory car insurance coverage required by law.
Collision coverage does not cover non-collision-related damage to your vehicle, such as theft, vandalism, or natural disasters. You would need comprehensive coverage, yet another type of car insurance.
Comprehensive Coverage
Comprehensive car insurance covers damage to your vehicle caused by non-collision events. This generally includes theft, vandalism, fire, and natural disasters. In Ontario, comprehensive coverage is optional and purchased in addition to the mandatory car insurance coverage required by law. Comprehensive coverage does not cover damage caused by an accident or collision. You would need collision coverage for that.
Specified Perils Coverage
Specified perils coverage protects certain types of damage to your car, such as fire, theft, vandalism, hail, lightning strikes, or explosions. It only covers the perils specifically listed in your policy and nothing else. As a result, this coverage is usually less expensive than comprehensive coverage. In Ontario, specified perils coverage is optional and typically purchased in addition to the mandatory car insurance coverage required by law.
Common Add-Ons
On top of your insurance coverage, many companies offer add-on services. However, this may increase the cost of your monthly premium. Common add-ons include;
- Roadside Assistance: Pays for towing services and other emergency help if your vehicle breaks down.
- Rental Car Coverage: Protects your rental car from damages due to an accident or other covered event.
- Extended Coverage: Increases the coverage limit in the policies of your choosing.
Where to Get Car Insurance Quotes
There are three broad options for where you can buy car insurance. The best choice will vary with your personal preferences. This section will walk you through each option and the requirements to get insured.
- Direct from the Insurer: The fastest way to get insurance is directly applying with a company. This is generally done online or through the phone. However, you will have little customization and could miss some great policies.
- Agent: Insurance companies also have agents if you need more assistance. They’ll guide you through all the offerings offered by the company. However, they won’t be experts in policies offered by other companies.
- Broker: Insurance brokers work with many companies and can help you compare policies. They offer the most selection and may help you find the cheapest policy. However, they often charge an additional fee.
Regardless of where you get car insurance, you must provide some basic information. Initially, you’ll need to provide personal information. This includes your diver’s license, address, age and gender. Insurers typically also want to know if you took driving school courses or have made any insurance claims.
Next, you’ll also need to provide information on your vehicle. This includes the year, make, model and kilometres. Also, expect to provide information on how you plan to use the car and estimate your expected annual kilometres.
Step-by-Step Guide To Getting Car Insurance In Ontario
Securing car insurance in Ontario doesn’t have to be a daunting task. With these steps in mind, you’ll be well-equipped to navigate the process, allowing you to cruise the open roads with confidence and peace of mind. Remember, the journey to finding the right car insurance policy is as much about safety and protection as it is about savings. Here’s how to get car insurance in Ontario:
Step 1: Understanding Your Needs
Before you start shopping around, it’s crucial to understand your own unique requirements. Evaluate how your car will be driven and consider who will be driving your car such as friends, family, and your children (when the time comes) as well as how often other people will need to drive your car.
Then reflect on the coverage level that will best fit your lifestyle and needs. Is the bare minimum enough, or would a comprehensive plan provide the peace of mind you’re seeking? Your answers will set the stage for your insurance shopping expedition.
Step 2: Embrace the Power of Research
The world of car insurance in Ontario is not a one-size-fits-all scenario. Each insurer has its own formula for calculating premiums, meaning rates can vary dramatically from one company to another for the exact same coverage. Turn detective and uncover what factors insurers consider when determining your rates – these typically include your driving history, the type of car you drive, your location, and the amount of coverage you select.
Step 3: Time to Shop Around
Now that you’re equipped with knowledge, it’s time to hit the (virtual) pavement. Use online platforms to instantly compare quotes from multiple insurance providers.
Look for a balance of reasonable cost and sufficient coverage. Don’t be shy to ask questions, either. The best insurance providers in Ontario will be transparent and ready to assist you.
Step 4: Seek Out Discounts
Insurers often offer a variety of discounts that you may be eligible for, such as those for being a safe driver, bundling multiple types of insurance, installing anti-theft devices, or for students with good grades. Be sure to ask about these potential savings when talking to insurance providers.
Step 5: Review and Confirm
Once you’ve narrowed down your choices, take a moment to review everything. Compare the final contenders, taking into account their coverage, cost, and customer service reputation. If you’re torn between options, it might be helpful to make a good old-fashioned pros and cons list.
Step 6: The Final Purchase
When you’re satisfied with your selection, it’s time to make the final purchase. Contact the insurance company to initiate the policy. They’ll walk you through the process and explain the necessary documents, which typically include your driver’s license, vehicle registration, and payment details. Once everything is submitted and approved, you’ll receive your insurance card or “pink slip” as proof of insurance.
How long will it take?
The actual time it takes can range from a few hours to a couple of days, depending on the complexity of your driving history and the efficiency of the insurer. Once you’ve provided all necessary information, received a quote, and agreed to the terms, your insurance company will process your application. In most cases, you can get an active car insurance policy the same day you apply, often in just a few short hours (or less!).
Once your application is successfully processed, your policy could be activated almost immediately. You’ll then receive your proof of insurance, or the coveted “pink slip,” which you should keep in your vehicle at all times. So, buckle up and enjoy the ride, because getting car insurance in Ontario can be as smooth as a Sunday drive through the countryside.
The Five Factors That Decide The Cost Of Car Insurance In Ontario
A higher probability of making an expensive claim will increase your insurance cost. Insurance companies evaluate loads of data to predict the likelihood of needing to make a claim. Most importantly, this includes your vehicle, driving record, neighbourhood, and personal details.
In addition, your coverage amount and deductible will influence the total payout your insurance provider may need to make. Your premium will increase with more coverage and a lower deductible. The remainder of this section goes deeper into each factor.
1. Vehicle
Some cars are more expensive to repair and replace. As a result, you’ll need to pay a higher premium. For example, a sporty model with several performance features will be more expensive to insure than a family sedan.
2. Driving Record
Your driving record can impact your insurance rate. You’ll likely get a lower premium if you don’t have any violations, such as speeding tickets or DUIs. This is because there is less probability of needing to make a claim.
In addition, insurance companies also review your demerit points. These are infractions added for breaking specific traffic laws. For example, making an improper right turn results in two demerit points, while you’ll get six points for careless driving. A higher amount of points will increase your insurance costs because you are deemed a riskier driver.
3. Neighbourhood
Your insurance premium will increase if your neighbourhood has a higher population density or an increased chance of theft and vandalism. For example, residing in a densely populated urban area will increase the number of cars on the road. This could increase the chance of a collision, resulting in more significant insurance premiums.
4. Personal Details
Details such as your age and gender are two key factors that can influence your car insurance premiums. For instance, insurance companies view drivers under 25 as riskier to insure due to their lack of experience behind the wheel and tendency to engage in risky driving behaviours. As a result, younger drivers typically pay higher insurance premiums than middle-aged drivers. Similarly, men are more likely to get into accidents than women, and this difference is reflected in their insurance premiums. Men usually pay more for car insurance than women.
5. Insurance Coverage
Your premiums will increase as you add more policies and coverage amounts. For example, adding collision coverage and roadside assistance will increase your premiums. This increases the amount your insurance company may have to pay.
In addition, a lower deductible will increase your premiums. Your deductible is the amount you’ll need to pay out of pocket when making an insurance claim after an accident. With a lower deductible, your insurance company will need to cover more expenses in the event of a claim.
How To Reduce The Premiums On Your Car Insurance In Ontario
Navigating the landscape of car insurance premiums in Ontario can feel challenging, but there are several effective strategies to help bring costs down. In this section, we’ll explore ways to reduce your auto insurance cost without compromising your coverage, offering you peace of mind while safeguarding your wallet.
Bundle with Home Insurance
One way to reduce the cost of premiums is by bundling with other insurance policies, such as home insurance. When you purchase multiple policies from the same provider, you can often get discounts of up to 20 percent off your total premium.
Increase Your Deductible
Choosing a higher deductible on your policy can reduce your premiums. A higher deductible means you’ll need to pay more out-of-pocket if you make an insurance claim, so you should only choose this route if you’re confident in your ability to cover the cost of repairs.
Increase Your Safety Ratings
Safety features like car alarms and anti-theft devices can sometimes qualify for discounts. This is because these features help to reduce the risk of theft or vandalism, making them less likely to result in large insurance payouts. Additionally, your insurance provider may offer discounts for courses on defensive driving and other safety topics.
Negotiate & Shop Around
It’s always worth contacting your auto insurance provider to see if they can offer you a better rate. Be sure to include pertinent details, such as recent improvements in your driving record and vehicle model. Additionally, be prepared to shop for different providers using an insurance broker.
Insurance brokers are professionals who can help to find the most suitable insurance policy for your needs. They work with multiple providers, allowing you to compare and contrast policies and coverage levels. This approach can reduce your monthly premiums without sacrificing quality coverage.
Some of the best car insurance companies in Ontario include:
Surex – Online Brokerage
Surex, a renowned Canadian insurance brokerage, prides itself on assisting customers in comparing car insurance quotes from Ontario’s top insurers, helping them find the ideal quote within ten minutes. This could save you hundreds of dollars each year.
The platform’s dedicated Licensed Insurance Advisors play a pivotal role in helping you through the entire process. They’ll even help you through the steps of making your final purchases, all through the website.
YouSet – Online Brokerage
YouSet is a distinguished insurance brokerage, serving clients in Ontario and Quebec. The platform is best known for comparing car and home insurance options that can save you up to 29% on the cost of premiums. With its cutting-edge technology, YouSet sifts through thousands of algorithms to pinpoint the best insurance quote tailored for you.
After responding to a handful of questions, YouSet’s advanced search technology takes over. The company guarantees a personalized auto insurance quote in less than four minutes. In addition to their online tool, YouSet’s helpful customer service team is accessible via online chat, email, and phone calls.
Belaire Direct – Insurer
Belairdirect is an Ontario and Quebec-based home and car insurance company. It offers various discounts to suit different drivers. Multi-vehicle customers can save up to 15% on their car insurance, and customers can access major savings when they bundle home and car insurance in Ontario.
Belaire also prides itself on first-rate customer service and has been awarded prizes for best call centre management. Some of Belairdirect’s service features include an online chat with certified insurance agents, free online quotes, and a 30-minute claims guarantee.
How to Make a Car Insurance Claim in Ontario
Paying for car insurance only benefits you if you correctly make a claim. Any mistakes in this process can result in an inaccurate payment. Follow these steps to make a car insurance claim properly:
- Contact your insurer immediately after the incident and explain what happened. Do not admit fault, as that could affect your eligibility for claims.
- Take photos of the damage and record any witness statements if possible. You can also take pictures of the accident, including any skid marks or debris.
- If the police were called to the accident scene, obtain a copy of the police report.
- Start a claim and provide the necessary information. Include the date, time, location, and any witnesses names and contact information.
- Your insurer will assign an insurance adjuster to investigate the incident and determine liability.
- They may request that you take your vehicle for an estimate or inspection by an appraiser if needed.
- Keep copies of all documents related to the accident and your claim, including estimates, repair bills, and any correspondence with your insurance company.
- Once all documents are received, they will process the claim and make any payments.
It is essential to know that you may need to pay a deductible before any claim payments are made. Furthermore, if the insurer suspects fraudulent filing, they may reject your claim. Read their policy and understand what is covered when making a car insurance claim.
Mistakes to Avoid
Don’t admit fault or make any statements about the accident to anyone other than the police or your insurance company. Only sign documents or accept settlement offers from the other driver’s insurance company after consulting with your insurance company or an attorney. Report the claim or provide your insurance company with the necessary information to process it. Don’t exaggerate your injuries or the damage to your vehicle. Remember to follow up with your insurance company if you are still waiting to hear back within a reasonable time.
